
Singapore Goods Import/Export Process, Taxes, and Requirements!
As one of Asia’s most resilient economies, Singapore maintains a stable and positive growth trend. In 2024, Singapore’s total external trade volume reached approximately SGD 1.3 trillion, including exports of around SGD 670 billion and imports of approximately SGD 630 billion.
For foreign trade enterprises, particularly those seeking to expand into overseas markets, understanding Singapore’s current trade industry data and customs policies is essential. Below is detailed information to help you navigate Singapore’s trade environment.
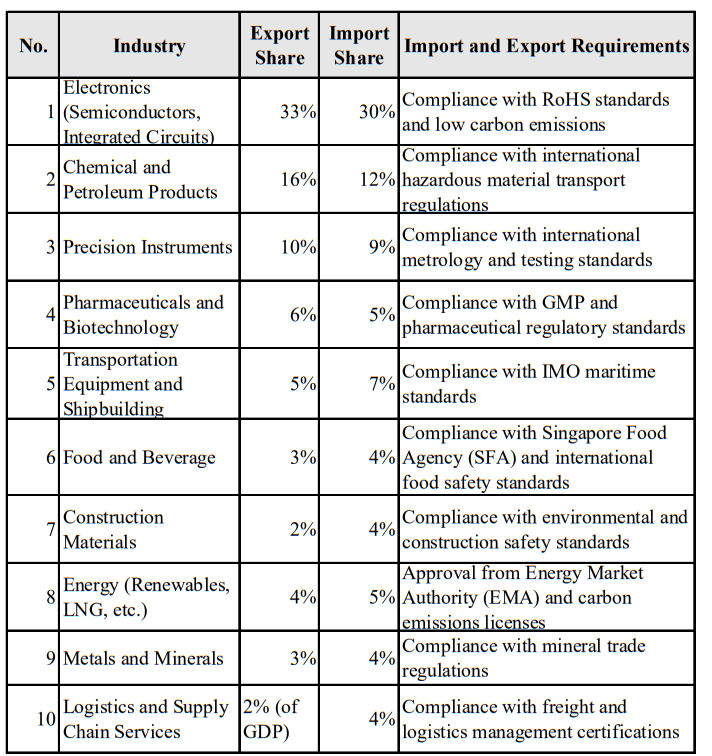
💡Top 10 Trade Industries and Import/Export Requirements
Singapore Customs Overview

Singapore Customs, under the Ministry of Finance, is the country’s trade regulatory and enforcement agency responsible for managing import and export regulations, tax enforcement, and trade facilitation.
Key Responsibilities
Enforce customs and trade laws to facilitate trade while ensuring tax collection and regulatory compliance.
💡 Resource Inquiry
Singapore Customs website provides comprehensive policy information, including tariff schedules, trade agreements, import/export restrictions, and declaration guidelines. (https://www.customs.gov.sg/ )
📦 Import and Export Policies and Processes
Import Process
Before importing goods into Singapore, importers must submit permit applications through TradeNet to Singapore Customs.
Step 1: Permit Application
● Importers must submit a permit application via the TradeNet system.
● Singapore Customs reviews the application and issues an import permit and delivery confirmation to ensure compliance.
Step 2: GST Payment
● All imported goods are subject to a 9% Goods and Services Tax (GST).
● Regulated goods require permits from relevant authorities in advance.
Export Process
Unregulated goods must have their permits submitted within three days of export through TradeNet.
Step 1: Permit Application
● For unregulated goods exported by sea or air, permit applications must be submitted within three days after export.
● Regulated goods require permits before export and approval from relevant authorities.
💡 Tip: Ensure compliance with destination export restrictions to avoid violations during re-export.
⚙️ Customs Clearance Process

1. Preparation Phase
● Product Classification: Determine HS codes for accurate declaration.
● Import Requirements: Verify the need for permits and compliance with specific standards.
● Document Preparation: Collect commercial invoices, packing lists, import permits (if required), and certificates of origin.
● Pre-Declaration: Submit a pre-import declaration through TradeNet.
2. Arrival Stage
● Arrival Notification: Shipping or airline companies submit arrival notices to Customs.
● Electronic Declaration: Submit a Customs Import Declaration (CID) via TradeNet.
● Tax Payment: Calculate and pay duties and GST.
3. Customs Review Stage
● Document Review: Ensure accurate information.
● Goods Inspection: Random or special inspections may be conducted.
4. Goods Release and Collection
● Release Notification: System generates a release notification.
● Collection: Importers collect goods upon notification.
5. Post-Release Procedures
● Final Declaration Submission: Complete within a specified timeframe.
● Record Keeping: Maintain all customs clearance documents for at least five years.
💰 Duties and Product Tax Rates

According to Singapore’s Customs Act, imported goods are divided into two categories:
1. Dutiable Goods: Include petroleum products, alcoholic beverages, tobacco, and motor vehicles.
2. Non-Dutiable Goods: All other goods fall into this category.
Tax Information:
● GST (Goods and Services Tax): All imported goods are subject to a 9% GST.
● Ad Valorem Duty: Some dutiable goods are taxed based on the value of the goods.
💡 Practical Tip: To check specific product tax rates, visit the Singapore Customs website for detailed tariff schedules.
🌍 Re-Export Trade Considerations
Singapore is a major hub for re-export trade. Here are some key considerations:
1. Ensure Legal Compliance:Re-exports involve regulations from multiple countries, and export-controlled destinations must be avoided.
2. Permits and Licenses:Multiple permits may be required for re-export activities; early application is advised.
3. Record and Audit Requirements: Maintain trade records for future audits.

🔑 Trade Facilitation Tips
● Leverage Singapore’s Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) to enjoy tariff reductions and lower trade barriers.
Optimize logistics costs by taking advantage of Singapore’s port infrastructure.
