
How Do Foreigners in Singapore Pay Their Personal Tax?
Do foreigners in Singapore need to file tax returns?

Singapore does not levy capital gains tax or inheritance tax.
All income generated in Singapore is taxable income and those working abroad are exempt from tax.
There are different tax rules for each individual depending on their tax resident status.
The deadline for filing individual tax returns is April 15 each year and income tax is calculated on the basis of the previous year.
If you have resided (except for reasonable temporary absence) or worked (except as a director of a company) in Singapore for more than 183 days in the year preceding the tax year, you are a “tax resident”and are subject to tax.
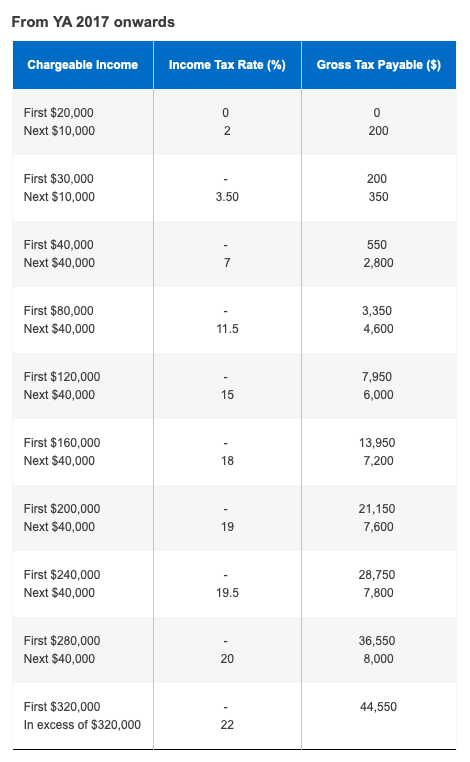
If you have resided in Singapore for more than 61 days but less than 183 days in the year preceding the tax year, you will be subject to the “non-tax resident” tax rules, ranging from 15% to 22%, to repay your personal income tax.
183 days refers to the number of days you stay in Singapore during your employment in Singapore, including weekends and public holidays. The period of stay is also counted when you are out of Singapore for a valid reason, such as an overseas vacation or business trip during your employment.
How much income do I need to report for tax purposes?

How to file your personal income tax return
Tax Return Forms at a glance. Tax Resident Individual – Form B1 Self-Employed – Form B Non-Resident Individual – Form M
After submitting your tax return, you will receive a notice of assessment or a tax bill from May to September.
Delay in filing tax returns (or failure to file) will result in a penalty. Please note that IRAS may take legal action against those who do not file tax returns or do not pay their taxes.
The tax bill will indicate the amount of tax you must pay. If there is a disagreement, you will need to notify the tax department within 30 days (from the date identified on the tax bill), stating the reason.
Regardless of whether you have notified the tax office of your objection, you are required to pay the full amount of taxwithin 30 days of receiving the notice of assessment.
After receiving the Notice of Assessment issued by the tax office, you can pay the tax in one of the following ways, depending on your situation.
– Automatic deduction (GIRO)
– Paynow (scan QRcode)
– Internet banking payment
– DBS Paylah
– Phone Banking (only for DBS/POSB, OCBC and UOB)
– Payment at ATM (only for DBS/POSB and OCBC)
– Bill payment on AXS online platform or AXS machines
– Self-service postal server (SAM) online platforms and sites
– NETS (Post Office Service Desk only)
– Credit card payment (AXS sites)
– Checks
– Wire transfer, VBOX
The tax office encourages taxpayers to choose the GIRO payment method, through which they can pay their taxes directly from their personal bank accounts, saving them the hassle of queuing up and will avoid the problems that may arise from payment delays, etc. The government also offers 12 months interest-free installments to taxpayers who choose GIRO.
Those who do not have a GIRO can request an application form from the tax office to apply for.

– Income earned through a partnership business in Singapore.
– Your overseas employment is also part of your Singapore employment.
– You are working overseas on behalf of the Singapore government.
How to declare taxable overseas income.
For taxable overseas income, you must report it under “Employment Income”, “Trading Income” or “Other Income” (whichever is applicable).

– Car and car-related benefits (e.g., a car provided by your employer)
– Monthly transportation allowance (mileage reimbursed if private car) and meals
– Reimbursement for medical and dental treatment for yourself and dependents
– Overtime
– Per diem (per diem for overseas travel)
Capital gains tax, inheritance tax, estate tax Capital gains are “investment income” from real assets, such as real estate, financial assets, etc. However, Singapore does not levy any capital gains tax.
In Singapore, inheritance tax, also commonly known as Estate Duty, is a tax that must be paid on property left behind by a person who passes away. However, Singapore has abolished Estate Duty in 2008.
